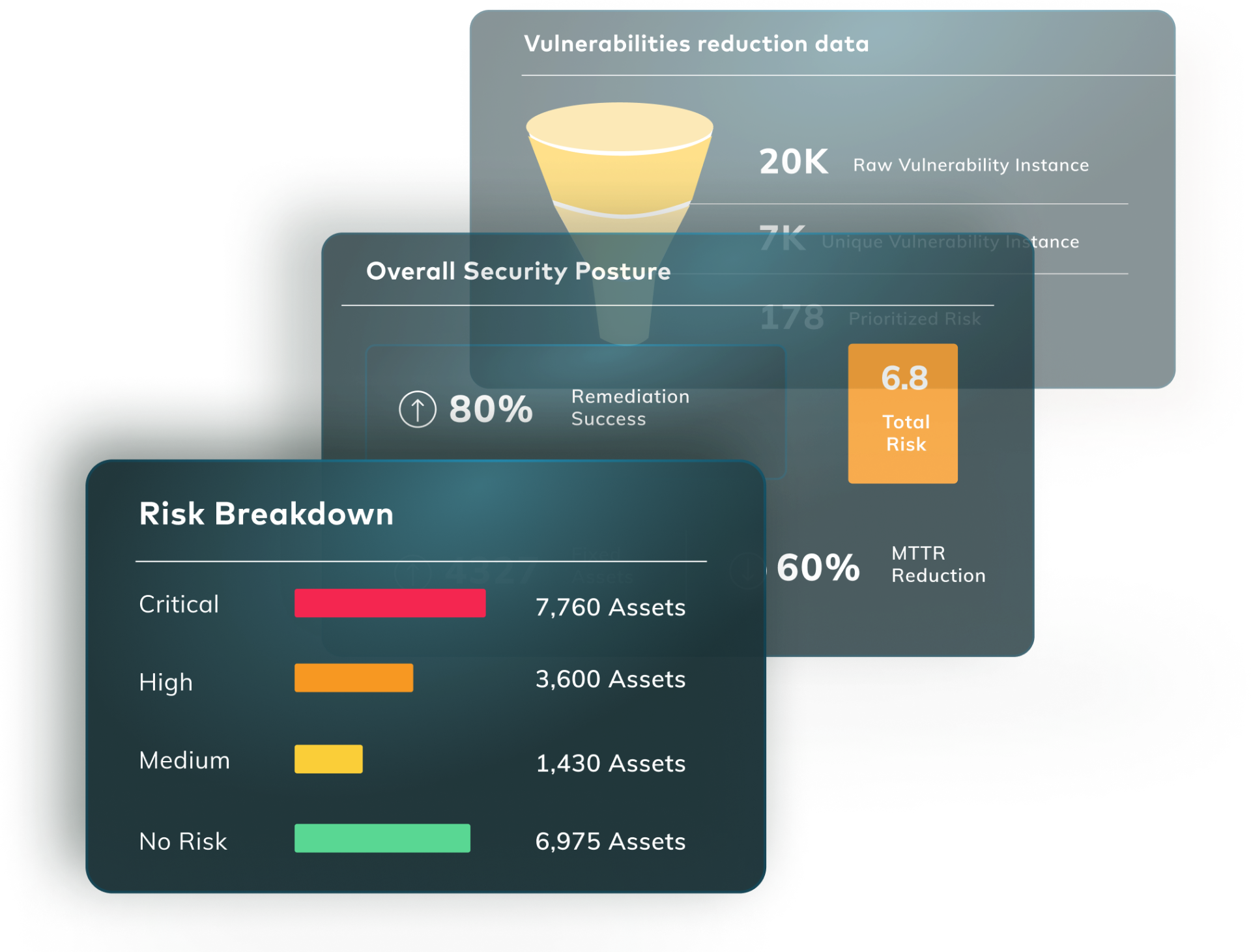
The business of vulnerability management across networks, clouds and applications tends to be a complex process that involves several stakeholders and demands multiple actions such as identifying, prioritizing, managing, and reporting vulnerabilities in your system.
Determining the success or failure of a vulnerability management program cannot be based solely on how many vulnerabilities were fixed in a day, week, or month—or without understanding the risks involved, and efforts that were made. Successful vulnerability management requires taking into account the wider cyber risk picture. It requires thoughtful planning and a clear roadmap, with defined steps.
Introducing the full vulnerability management lifecycle, step-by-step
Step 1: Consolidation
Key statistics: 60% of organizations use at least 2 scanners to identify vulnerabilities.
As the attack surface continues to expand, and new vulnerability and risk types emerge, it becomes harder to manage the enormous volume of scan data.
There can be a tendency to believe that the optimal solution is always just one tool away. However, continuously adding more tools to a security technology stack can eventually hinder the effectiveness and cost-efficiency of an organization. The issue of tool sprawl is a major concern for today’s security leaders.
Centralization of vulnerability and cyber risk data in one place, is the first, and fundamental step in the cyber risk lifecycle.
Why?
- For complete visibility
- For duplicate data governing
- For better control
Watch: an integrated approach to cyber risk management >>
Step 2: Correlation
Key statistics: 66% face a backlog of more than 100,000 vulnerabilities.
Duplicate data not only means duplicate tasks and inefficiencies, but also limited understanding of actual risk. In times when scale is crucial, businesses can’t afford chasing after individual vulnerabilities. The 2nd step in the cyber risk lifecycle is all about vulnerability deduplication and clustering. It is essential to view vulnerabilities not simply as individual issues, but as groups of common weaknesses that can be fixed with the same strategies or mitigating actions.
Vulnerability correlation is the process of identifying and analyzing multiple vulnerabilities within a system or network to determine their potential impact and prioritize remediation efforts. It involves identifying how different vulnerabilities can be combined and exploited by attackers to launch an attack on the system. By correlating vulnerabilities, security teams can develop a more comprehensive view of the potential threats and prioritize their responses accordingly.
Correlating our data allows us to take action on unified entities, rather than disparate and often overlapping cyber risk concerns. Effective deduplication methods can be based on asset attributes, affected software or CVEs.
Why?
- For simplified scan data management
- For accurate risk understanding
- For improved operating efficiency
Read: Cyber risk in 2022: A 360° view (and trends for 2023) >>
Step 3: Enrichment
Key statistics: 55% think their threat intelligence is not predictive enough.
Lack of context is one of the biggest enemies of a successful cyber risk management program. Context means understanding the specific impact of vulnerabilities on the organization’s risk posture, And how to act upon them. The next step in the cyber risk management lifecycle is enriching the correlated scan data with actionable information with threat intelligence sources, root cause analysis, remediation intelligence and attacker path context.
Why?
- For accurate risk scoring
- For better actionability
- For effective and smart prioritization
Learn: Mapping CVEs to the MITRE ATTACK framework >>
Step 4: Prioritization
Key statistics: 79% agree that their vulnerability prioritization doesn’t consider the business context.
The identified, correlated and enriched vulnerabilities should now be organized into a prioritized list that matches the risk-based policies each organization determines.
There are several factors that can be considered when prioritizing vulnerabilities, such as the level of access required to exploit the vulnerability, the potential impact on data confidentiality, integrity, and availability, the level of effort required to exploit the vulnerability, and the availability of patches or other remediation measures.
But while relying on CVSS, EPSS and other standard risk scoring methods is important, it’s not enough. Prioritization must also involve assessing the business impact of potential exploitation, such as financial losses, reputational damage, and regulatory non-compliance. Effective vulnerability prioritization helps organizations to make informed decisions about which vulnerabilities to address first and how to allocate resources for maximum impact.
Identifying the most important vulnerabilities for your specific organization is key, and prevents wasted time and effort on prioritizing vulnerabilities ineffectively so that focus remains on remediation. This is where customized risk scoring can come into play.
Why?
- For risk-based prioritization
- For efficient operations
- For rapid mitigation
Watch: Reducing the burden of vulnerability management at scale >>
Step 5: Orchestration
Key statistics: By 2025, 90% of security operations workflows will be automated and managed as code.
The next step, after assessing which vulnerabilities demand more attention, is to orchestrate the entire mitigation operation in the most efficient way possible. There are a lot of moving parts, multiple stakeholders involved, and this is where automation becomes crucial. Automating the communication and collaboration remediation tasks is key to streamlining risk mitigation.
Vulnerability management orchestration enables security teams to provide real-time visibility into the status of vulnerabilities and remediation efforts, as well as providing insights and analytics that can be used to optimize vulnerability management operations.
Why?
- For effective operations
- For reduced MTTR
- For better organization-wide collaboration
Watch: Reducing the burden of vulnerability management at scale >>
Step 6: Collaboration
Key statistics: Responsibility is placed on IT organizations for remediation activities such as patching (63%) and configuration management (65%).
Cyber risk is business risk, and risk mitigation has become an organization-wide effort, creating too many cooks in the kitchen. DevOps, SecOps, and application development teams are now more than ever responsible for hands-on remediation tasks. The collaboration step is ensuring we manage the communication between all teams with the right tools, in the right way.
Collaboration is essential in ensuring that all stakeholders are aligned in their understanding of the risks and impact of vulnerabilities, and that remediation efforts are coordinated across teams and systems. It also helps to build a culture of security across the organization, with all stakeholders taking ownership and responsibility for their role in managing vulnerabilities.
Why?
- For faster resolution
- For breaking the silos between departments
- For better management and visibility
Learn: How you can achieve vulnerability management maturity >>
Step 7: Reporting
Key statistics: 60% agree that InfoSec teams are responsible for vulnerability reporting.
The next, and final** is reporting: Which vulnerabilities were fully remediated? Which ones got a workaround? Are there any vulnerabilities that haven’t been fixed or any areas in the system yet to be checked? Cyber security efforts are sometimes missed when there’s no proper reporting in place.
Vulnerability management reporting is the process of creating and distributing reports that provide an overview of the vulnerabilities identified in an organization’s systems, as well as the status of remediation efforts. These reports may include information such as the number and severity of vulnerabilities identified, the systems and applications affected, the current status of remediation efforts, and the effectiveness of those efforts.
Why?
- For better organization-wide collaboration
- For tracking progress and performance
- For meeting remediation SLAs
Watch: The ROI of Managed Risk-Based Vulnerability Management >>
Next steps
**Although It may seem like reporting is the final step of the cyber risk management lifecycle, it might actually serve as the very beginning, and get us back to step 1. The cyber risk management lifecycle should be considered as a loop – it never actually ends.
Setting a formalized plan and structure for your cyber risk operations is key to owning your risk.
The Vulcan Cyber® risk management platform helps security teams get their cyber risk together using vulnerability and risk correlation, prioritization and orchestration capabilities.
Get started today:
- Sign up for Vulcan Free
- Follow the latest cyber risk trends and insights
- Watch a demo of the Vulcan Cyber platform
- Or, schedule a demo
A Demo of Risk-Based Vulnerability Lifecycle Management in Action