-
Platform
OVERVIEW
Capabilities
-
Solutions
USE CASES
-
Cyber Risk Hub
LIBRARY
-
Company
GET TO KNOW US
-
Pricing
Learn about emerging threats such as the top 10 LLM risks and how you can take proactive measures to secure your software supply chain.
Malicious LLMs and other AI-generated attacks are leading the new wave of emerging threats. Continuous threat exposure management (CTEM) is an effective way to combat emerging threats.
4 emerging software supply chain threats to be aware of include:
An exposure management platform can help organizations prioritize and mitigate emerging threats.
It doesn’t matter how much you invest in cybersecurity tools or how many tools you have integrated into your IT, the main purpose is to protect your organization and resources from emerging threats. Emerging threats are tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used to exploit vulnerabilities in an organization’s security posture.
Organizations must be updated on the latest CVEs as they might compromise system integrity and potentially leak sensitive data into the wrong hands.
A data breach can come from the smallest cloud misconfiguration or lack of policy implementation. Emerging threats such as AI-generated phishing attacks, insider threats, zero-day exploits, and software supply chain attacks can wreak sheer havoc on an organization’s security posture.
Which leads to the bigger question.
Is your organization fully equipped to handle these threats? Beyond the basics?
This blog will examine emerging threats and LLM risks that might impact your software supply chain and how to prevent these attacks.
AI is a hot topic right now in the field of cyber security. The Vulcan Cyber Voyager18 research team found exploits in cyber security vulnerabilities via LLM agents that raised a few red flags. These types of emerging threats present security professionals with a score of new challenges and critical vulnerabilities that weren’t previously anticipated.
AI has ushered in a new wave of emerging threats.
AI-generated threats are becoming increasingly harder to detect and mitigate. Our research team also noticed threat actors leveraging LLM agent integration for remote code execution (RCE), which enables malicious attackers to gain unauthorized access to systems and execute arbitrary code on the organization’s networks and devices.
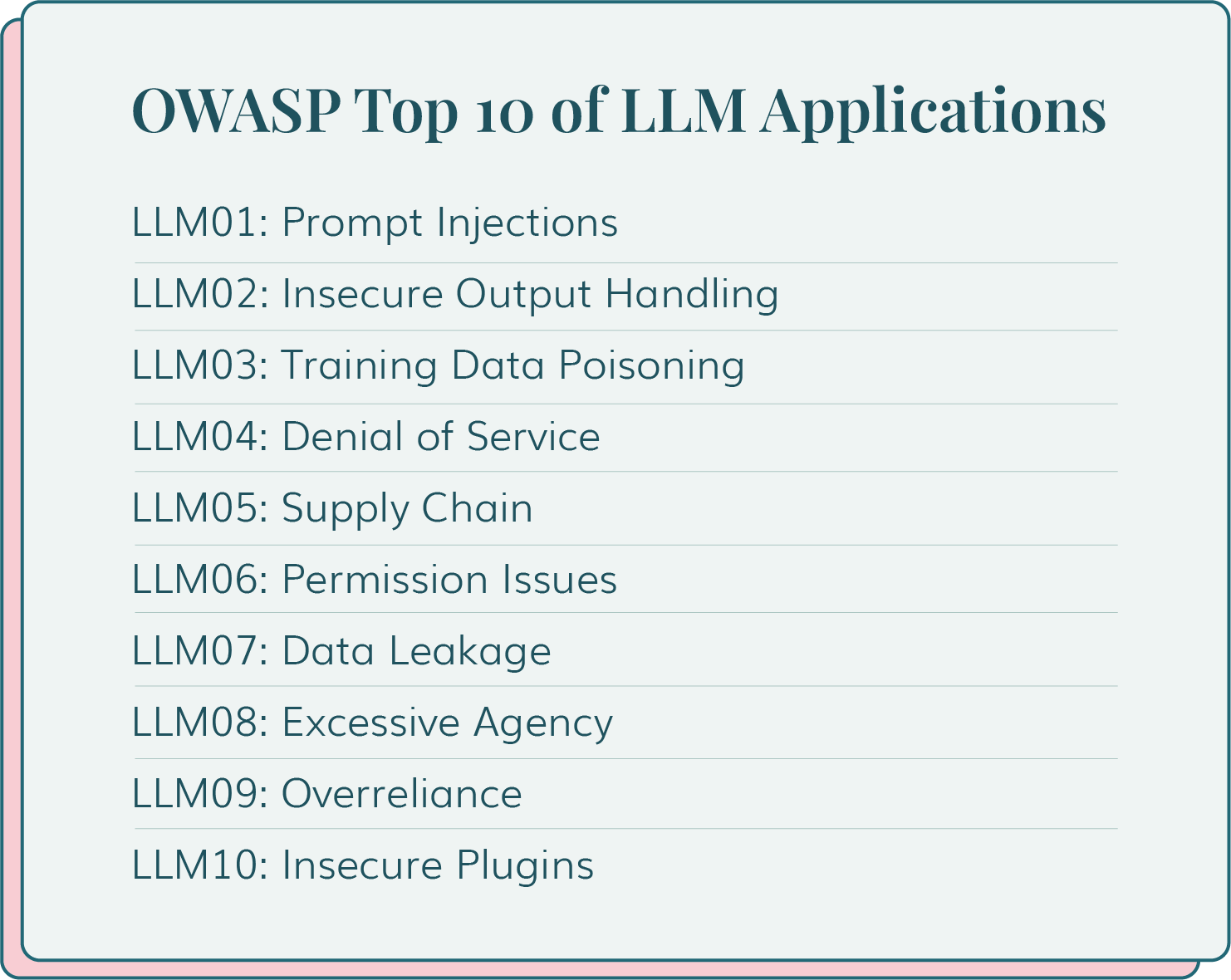
Prompt injections top the list of LLM threats and for good reason. They are exceptionally difficult to detect as threat actors can manipulate responses and exploit the context of the prompts for their benefit.
For example, in the software supply chain, prompt injections can target CI/CD pipelines and introduce malicious code. Organizations will have to tighten software supply chain security and implement a system for combating threat exposure, such as CTEM.
Is there a way to prevent these types of AI-fueled emerging threats? CTEM is a good start.
Continuous threat exposure management (CTEM) is a proactive cyber security program aimed at preventing emerging threats, such as malicious LLMs, through a 5-stage strategic approach.
The five stages of CTEM
|
Scoping Understanding the current risk posture |
Discovery Identifying the most critical assets at risk |
Prioritization Focus mitigation efforts based on context and risk level |
Validation Evaluate the likelihood of a breach and the effectiveness of security controls |
Mobilization Alignment of program and mitigation options |
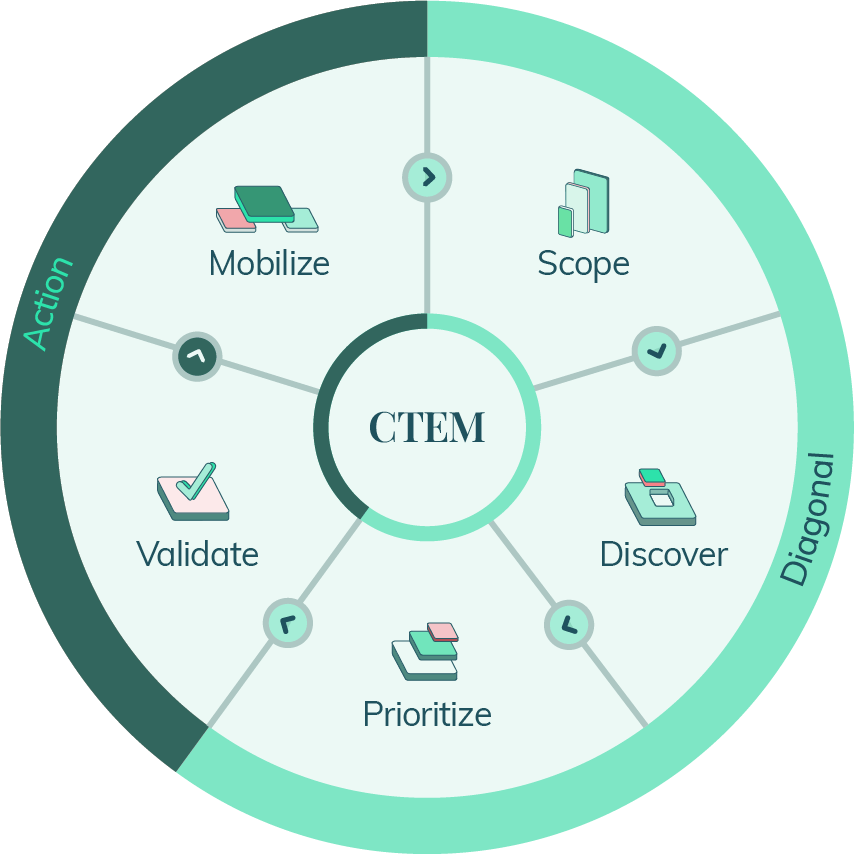
CTEM plays a significant role in minimizing the threat attack surface. CTEM can also correlate known threats within the organization’s critical assets, identifying areas at the highest risk of exploitation that require immediate attention and mitigation strategy deployment.
Watch >> The exposure risk management evolution in 2024
Is CTEM a good start? Yes. But what about emerging threats against software supply chains?
Attacks against software supply chains are soaring. In fact, Gartner predicts that by 2025, 45% of organizations worldwide will have experienced attacks on their software supply chains, a three-fold increase from 2021.
Key Statistics: Nearly 49% of organizations are vulnerable to a dependency confusion attack
Here are 4 emerging software supply chain threats you need to be aware of, including actionable mitigation steps The Vulcan Cyber team suggests.
Research found that nearly 49% of organizations are vulnerable to a dependency confusion attack. Dependency confusion attacks are a type of software supply chain attack where malicious packages are uploaded to public repositories with names identical to private dependencies, such as npm or PyPI. Cybersecurity researchers also identified a set of 116 malicious packages on the PyPI repository, designed to infect Windows and Linux systems with a custom backdoor.
The issue is that most package managers extract the latest version of a package by default, regardless of whether it comes from a public or private repository. Developers might download that malicious package and unknowingly disrupt the organization’s entire software supply chain.
Always download dependencies from the official repositories. Vulcan Cyber advises using lockfiles and scoped packages while regularly monitoring all dependencies for any unexpected changes.
Read more >> The complete guide to open-source security
A recent study showed a 28% increase in the number of malicious packages across open-source repositories in 2023. Attackers exploit vulnerabilities in build tools, such as compilers or package managers, and inject malicious code. Malicious code can linger around and remain undetected for long periods, potentially compromising the entire security of the software supply chain. Injected code can also exfiltrate sensitive data and lead to major breaches if left undetected.
The 2020 SolarWinds Supply Chain Attack is a good example of this type of threat. Malicious actors injected a backdoor into the Orion software updates, which impacted thousands of customers, including several U.S. government agencies.
Vulcan Cyber suggests isolating build environments and using only verified sources for downloading build tools. Stringently review all third-party plugins and dependencies used in the build process to ensure they do not contain malicious code.
Developers rely on CI/CD pipelines to automate the process of integrating code changes, running tests, and deploying applications, ultimately accelerating overall time to market. Attackers look for any security gaps to introduce malicious dependencies into the CI/CD pipeline, either by compromising public repositories or through tainted packages.
Poisoned Pipeline Execution (PPE) is another common attack where threat actors manipulate the pipeline’s configuration or scripts to insert harmful code during the build or deployment phases. Here is the full list of the OWASP Top 10 CI/CD Security Risks that you should be aware of when securing builds and ultimately, your entire software supply chain.
Don’t take those risks. Vulcan Cyber recommends using tools such as SCA, SAST, and DAST to scan dependencies for known vulnerabilities early in the building phase of the SDLC. Conduct thorough code reviews of build and deployment scripts to detect and prevent malicious modifications.
Key Statistics: Zero-day exploits on vulnerabilities within third-party code accounted for 41% of exploits.
A recent study found that 91% of organizations have experienced a software supply chain incident in the past 12 months. The same report found that the most common security incident was zero-day exploits. Data showed that zero-day exploits on vulnerabilities within third-party code accounted for 41% of exploits. Zero-day exploits target vulnerabilities in software or systems that are not yet known to the vendor or the public.
This situation presents a significant challenge for both C-level executives and security practitioners. Executives are responsible for acknowledging and addressing any zero-day exploits that could potentially impact customers. Meanwhile, the CISO and their security teams are expected to mitigate these vulnerabilities as quickly as possible, before any news goes public.
Quite the dilemma. The solution? Take preventive security measures in advance.
Here are a few suggested best practices:
Read more >> Securing the software supply chain: evaluating risk through attack path analysis
Although it certainly helps to apply all of the best practices mentioned above, it’s still not enough to protect against emerging threats.
The added element of AI has further heightened the risks of emerging threats in and around the software supply chain and critical assets floating around various cloud environments or applications. Outdated technologies and practices simply weren’t built with the concept of AI-generated attacks in mind.
That’s why you need to manage your exposure risk from end to end.
Get proactive exposure management for cyber risk reduction with Vulcan Cyber. Vulcan Cyber provides comprehensive visibility into your network, cloud, and application assets. Prioritize vulnerabilities and other emerging threats based on severity and focus mitigation efforts on actual business risk across all attack surfaces.
Close off security gaps and other possible attack paths with Vulcan Cyber.
Ready to own exposure risk? Get a demo and find out how you can prevent emerging threats and own exposure risk today.