-
Platform
OVERVIEW
Capabilities
-
Solutions
USE CASES
-
Cyber Risk Hub
LIBRARY
-
Company
GET TO KNOW US
-
Pricing
Key insights from IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach 2024, including rising costs, AI’s role, shadow data risks, and mitigation strategies.
As data breaches grow in frequency and sophistication, the financial and reputational impacts on organizations are skyrocketing.
The IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2024, conducted by the Ponemon Institute, reveals the true cost of these incidents and identifies key trends that shape the cyber security landscape.
This year’s report, based on data from 604 organizations across 17 industries and 16 countries, highlights the rising financial burden of breaches, the importance of AI in reducing damage, and the growing pressure from the cyber security skills gap. Let’s dive into the major insights from the report and what they mean for businesses today.
IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report 2024 reveals a 10% spike in average breach costs, reaching $4.88 million. AI and automation help reduce costs, while shadow data and cyber security skills shortages are driving them up.
The report also highlights the significant impact of business disruption, the importance of law enforcement in ransomware cases, and the continued vulnerability of the healthcare sector. Organizations must prioritize proactive security measures to mitigate these rising risks.
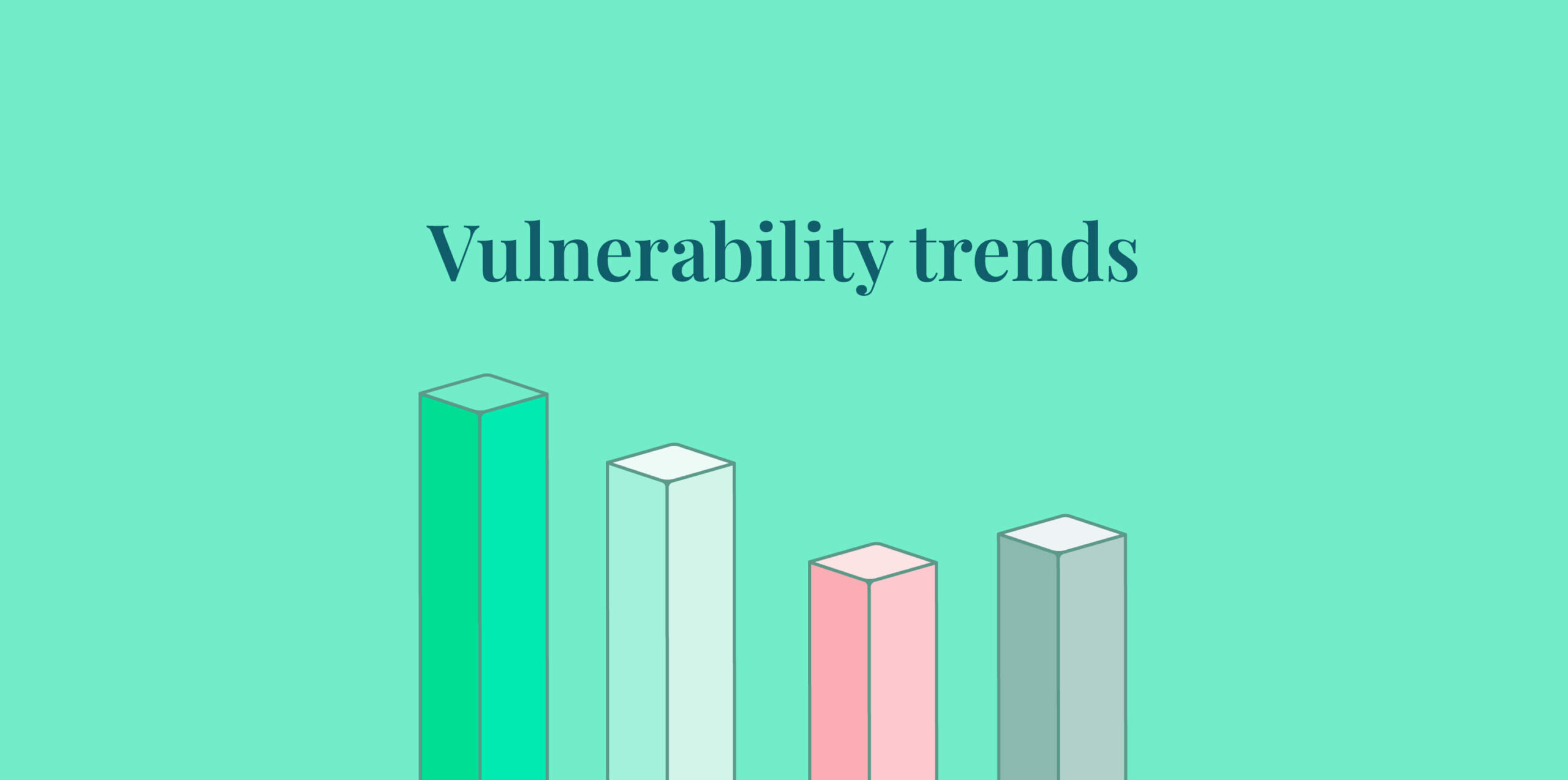
The global average cost of a data breach surged to $4.88 million in 2024, reflecting a 10% increase from 2023—the largest annual spike since the pandemic.
This rise is primarily driven by the costs associated with business disruption, lost customers, and post-breach responses, such as regulatory fines and customer remediation efforts.
Additionally, the lingering effects of inflation and the complexities of securing modern IT environments have contributed to these rising costs. The increasing reliance on data across industries means that breaches not only affect systems but also lead to massive operational disruptions that drive up expenses.
AI and automation are proving to be the most effective tools for reducing the financial impact of data breaches.
$2.2m
According to the report, organizations that deployed security AI and automation extensively across their operations saved an average of $2.2 million compared to those that did not.
his 45.6% reduction highlights the importance of leveraging AI for functions such as threat detection, investigation, and response.
AI enables security teams to act faster and more efficiently, reducing the time to identify and contain breaches, which in turn lowers the overall costs. For organizations seeking to mitigate the damage of a data breach, investing in AI is no longer optional—it’s essential.
The cyber security skills shortage is worsening, with 53% of breached organizations reporting that they faced significant staffing shortages in 2024, up from 42% in 2023.
This shortage correlates with higher breach costs—organizations with severe staffing gaps faced an additional $1.76 million in breach-related expenses. The report emphasizes that while AI and automation can alleviate some of the workload, they are not a replacement for skilled security professionals.
Organizations that invest in developing and retaining cyber security talent will be better positioned to detect, prevent, and respond to breaches more effectively, helping to reduce financial damage.
One of the most pressing issues highlighted in the 2024 report is the growing prevalence of shadow data—unmanaged or unauthorized data stored in various locations without the knowledge of IT departments.
35%
of data breaches involved shadow data, and breaches involving this type of data led to a 16% higher cost on average.
Because shadow data is often invisible to security teams, it’s difficult to track, classify, and secure, increasing the risk of breaches.
With data storage now spread across multiple environments, including public clouds, private clouds, and on-premises servers, organizations must prioritize data visibility and control to prevent breaches and minimize costs.
The most common attack vector in 2024 was the use of stolen or compromised credentials, accounting for 16% of all breaches.
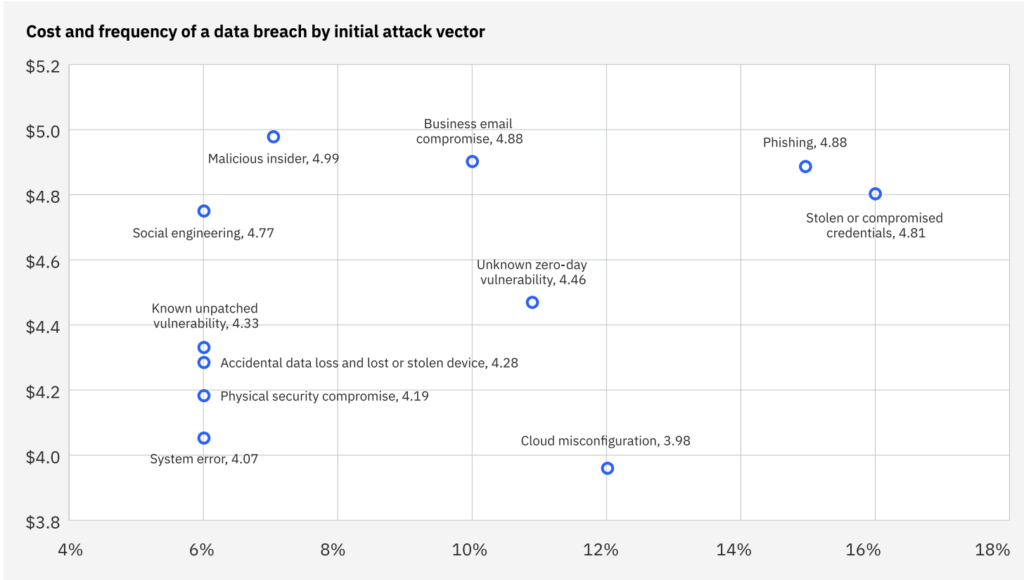
Credential-based attacks also took the longest to identify and contain—an average of 292 days—resulting in some of the highest breach costs.
Attackers can use stolen credentials to gain access to sensitive systems without triggering immediate alarms, making these types of breaches harder to detect.
Organizations must implement stronger authentication measures, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), to prevent credential-based attacks and reduce the time it takes to respond to breaches.
For the 14th year in a row, the healthcare industry experienced the highest average data breach cost, with breaches costing an average of $9.77 million.
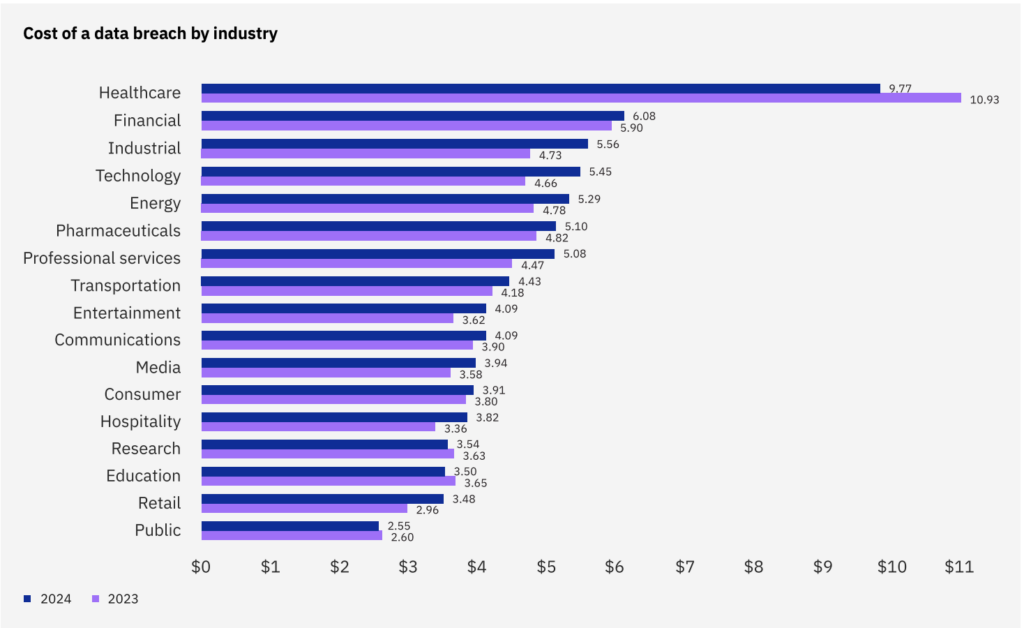
While this represents a 10.6% decrease from 2023, healthcare organizations remain highly vulnerable due to their reliance on outdated technologies and the sensitive nature of patient data.
The financial and operational disruptions caused by breaches in healthcare can have severe consequences, potentially putting patient safety at risk.
As healthcare continues to be a prime target for attackers, it’s crucial for these organizations to modernize their cyber security infrastructure to better protect patient data and reduce breach costs.
Organizations that involved law enforcement in ransomware incidents saw significant cost reductions.
$1m
According to the report, involving law enforcement saved organizations nearly $1 million on average, and 63% of those organizations managed to avoid paying the ransom.
Ransomware attacks are becoming increasingly common, and involving law enforcement early can help organizations recover data more quickly, reduce breach lifecycle times, and avoid ransom payments.
However, only 52% of organizations currently involve law enforcement, indicating a need for greater collaboration between businesses and law enforcement agencies to mitigate the costs of ransomware incidents.
Seventy percent of organizations in the 2024 study experienced significant business disruption following a data breach, with those disruptions leading to higher costs.
The average breach cost for organizations reporting substantial disruptions was $5.01 million—7.9% higher than for those with low disruption. Business disruption includes downtime, lost productivity, and diminished customer trust, all of which can have long-lasting effects.
For many companies, the financial damage from disruption far exceeds the initial cost of remediation, making it critical to have comprehensive incident response plans in place to minimize downtime and recovery times.
Another notable trend in the 2024 report is that 63% of organizations planned to pass the costs of a data breach onto their customers through price increases—up from 57% in 2023.
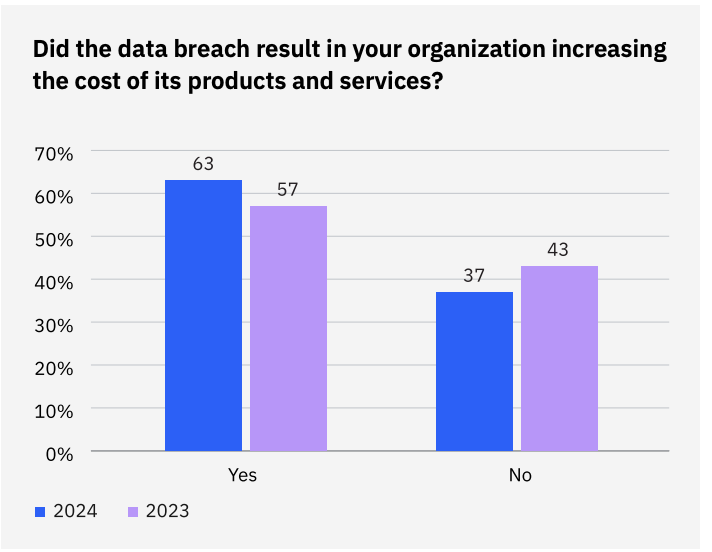
With rising operational costs and regulatory fines, many businesses are opting to increase prices for their products or services to recover some of the financial damage.
However, this strategy comes with risks, particularly in competitive markets where customers are sensitive to price changes. Organizations that choose this route must weigh the potential loss of customers against the need to cover breach costs.
Mega breaches, defined as those involving more than one million compromised records, are relatively rare but incredibly costly.
The report found that breaches affecting between 50 and 60 million records cost organizations many times more than the global average of $4.88 million.
Even the smallest mega breaches—those involving 1 to 10 million records—were nearly nine times more expensive than the average breach.
While mega breaches represent only a small fraction of incidents, their catastrophic financial impact highlights the need for organizations with large datasets to invest heavily in breach prevention and mitigation strategies.
The IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2024 offers a stark reminder of the growing financial and operational risks posed by data breaches.
As breach costs continue to climb, organizations must adopt more proactive measures, including the use of AI and automation, enhanced data visibility, and stronger authentication practices.
The report’s findings also underscore the importance of addressing the cyber security skills gap and involving law enforcement in breach response efforts.
With the landscape only becoming more challenging, businesses must prepare not just for the possibility of a breach but for the long-term consequences of one. By investing in the right tools and strategies now, organizations can better protect themselves from the escalating costs of data breaches in the future.