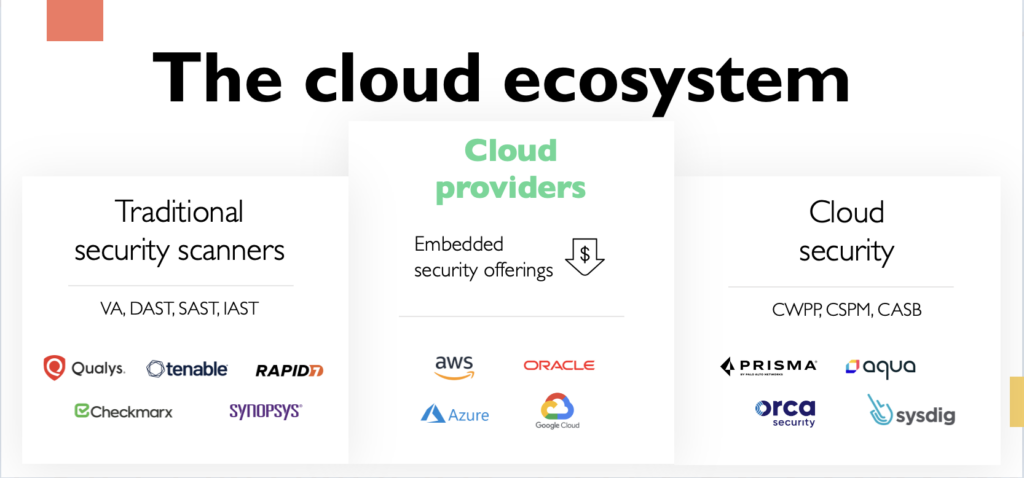
The major cloud service providers (CSPs) and other tech giants are stepping up their security game – introducing native offerings to aid their customers in the face of cloud migration challenges. In this blog post, we’ll cover the world of cloud security. Its early days, where it’s headed, and what users can do to stay ahead.
The beginnings of cloud security migration
As cloud providers emerged, more companies migrated their workloads to the cloud. The shift meant that security became a primary concern for customers looking to protect their and client data.

Following AWS‘ lead, Google and Microsoft added their own embedded security solutions to help users protect their data. Google’s On-Demand Scanning and Azure’s Security Center both offer built-in scanning capabilities. Finally, Oracle is the latest provider to join the party, with an embedded scanner for their own infrastructure instances.
The bait for cloud migration: Low prices and free trials
A likely reason for the addition of native security tools could be the emergence of third-party cloud security posture management (CSPM) products. Cloud security providers seek a way to claw back business, and so develop their own solutions.
From an end-user perspective, customers welcome these additions. The need is clear: simplified and unified security in cloud repositories storing their most valuable data.
This is why, while differing in their security features and capabilities, cloud providers all share one thing: lower price tags. They realize that security is the main barrier preventing migration to the cloud. And offerings like native security tools, for free, will only make their customers’ lives easier.
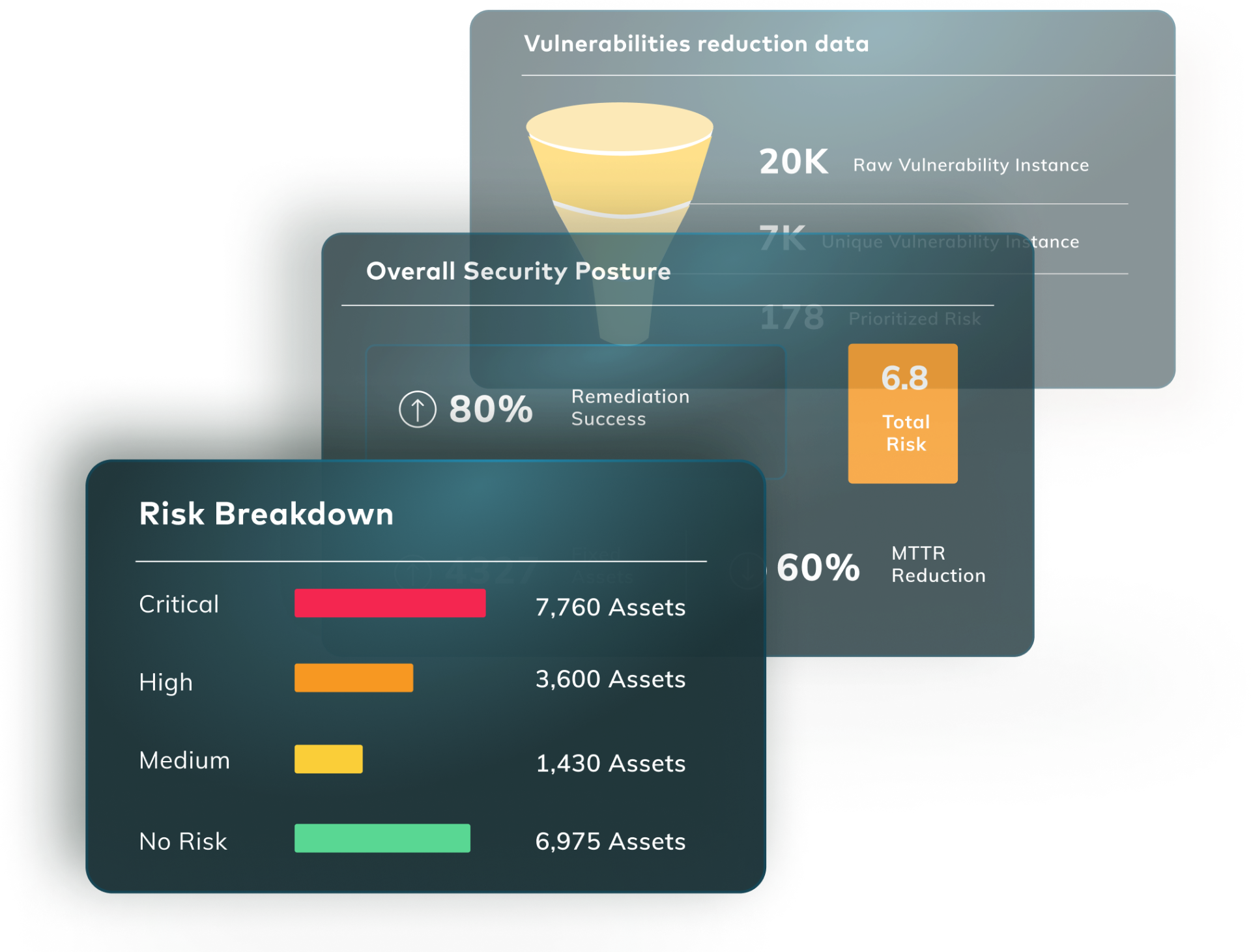
The growing simplicity of cloud security efforts frees users to invest in more impactful stages of the remediation lifecycle. These go far beyond just scanning and identifying problems.
Actionable cloud security
CSPs offering native vulnerability assessment empowers you to shift your team’s focus to the next phase. Specifically, what happens after vulnerabilities are identified?
We call this the post-scanning phase. It involves:
- Asset management
- Vulnerability prioritization
- Managing collaboration between different departments (IT, DevOps etc.)
- Remediation performance tracking
- Reporting
- Automation whenever possible
This is where post-detection tools become critical to achieving risk remediation success. Platforms like Vulcan Cyber® work hand-in-hand with cloud providers’ native vulnerability scanners. They turn an overwhelming flood of raw vulnerability data into coherent, prioritized action items. They even create tickets, using automation to guide your team through the relevant remediation stages.
Get started for free with the Vulcan Cyber end-to-end risk remediation platform. Request a demo or try Vulcan Free, and get fix done.