Vulnerability management (VM) stakeholders continue to struggle to keep up with the criminals, mainly due to the growing volume of attacks, and the lack of cyber security automation. According to Edgescan, on average it takes organizations 84 days to remediate high risk vulnerabilities—an almost three-month window during which networks and data can be compromised. The factors that constrain VM agility include:
- Siloed teams
- Manual processes
- Non-contextual scan data
- Complex environments
- Fragmented tool stacks
The strategies that organizations must embrace in order to achieve VM scalability and repeatability are centralization, orchestration, and automation. This blog post focuses specifically on the intersection of cyber security automation and vulnerability management. It describes how cyber security automation enhances VM scalability by eliminating tedious error-prone manual processes, promoting collaboration across teams, and shortening time to remediation. We examine which VM processes can and should be fully automated, and others where at least partial security automation is possible.
1. Automated Data Aggregation and Correlation
A key challenge encountered right at the beginning of the vulnerability management workflow is the numerous and diverse streams of scan and monitoring data that often obscure more than they reveal. Each of the many types of scanners deployed has a unique set of metrics and log data structure. Gaining timely and actionable insight into a system’s overall security posture status requires an experienced and skilled vulnerability management specialist.
The solution:
Automatically aggregate all scan and test results into a central repository where advanced data technologies normalize and correlate the data into a real-time, dynamic understanding of security posture issues.
In a use case proposed by Optiv to accelerate vulnerability management, the Vulcan Cyber risk remediation platform is integrated via API with both a Tenable vulnerability scanner as well as with Microsoft’s system center configuration manager (SCCM). The central Vulcan Cyber repository combines the Tenable vulnerability data from the Windows desktops and servers scanned with the host information from SCCM in order to continuously assess the system’s security posture.
Tip:
In today’s dynamic environments auto-discovery of assets is essential to ensure end-to-end vulnerability management coverage. Auto-discovery also quickly detects “forgotten” assets that needlessly increase the organization’s attack surface.
2. Automated Prioritization
The next major challenge in the vulnerability remediation workflow is to effectively prioritize the many vulnerabilities detected. After all, not all vulnerabilities are created equal; they range from false positives that can and should be ignored to high-risk vulnerabilities that present a real and immediate risk to the organization’s security posture. With a typical organization facing tens of thousands of vulnerability instances at any given point in time, relying solely on the technical risk scores assigned by public vulnerability databases such as CVE and NVD is not an effective prioritization strategy.
The solution:
Smart, organization-centric prioritization that enriches CVE scores with both internal business data and external data such as threat intelligence and vendor guidelines.
Vulcan Cyber, for example, automatically and continuously ingests asset data from the organization’s Ivanti or SCCM asset discovery and patch deployment framework. Vulcan then automatically prioritizes remediation tasks by identifying which of the vulnerabilities detected for these assets pose the highest risk in light of data enrichment, such as context, business logic, and threat intelligence. By highlighting the organization’s biggest risks, Vulcan Cyber allows teams to run effective vulnerability remediation programs at scale by focusing remediation efforts on the vulnerabilities that matter most.

Tip:
Tight integration with back-end systems such as asset management and change management databases provides important prioritization insights and closes feedback loops.
3. Automated Ticketing
One of the biggest vulnerability remediation bottlenecks is ticket management. It is very time-consuming and unscalable to manually open and assign remediation tickets for each detected vulnerability, track their progress, and then close those tickets when done.
The solution:
Automated opening of tickets in SOAR/SIEM tools and assignment to the right person/team. As the remediation process unfolds, there are automated handoffs among teams, culminating in automated verification of ticket closure when the process is complete.
Vulcan Cyber, for example, integrates bi-directionally via API with Jira or ServiceNow so that playbooks can automatically open and assign vulnerability remediation tickets, as well as orchestrate all remediation steps including closing a ticket after the required action has been validated and verified. At all times, teams have access to intuitive ticket status and progress reports. The platform provides out-of-the-box playbooks that are easily customized, or users can create their own playbooks from scratch.
Vulcan’s automated ticket creation and management capabilities scale up and streamline the vulnerability remediation process while providing all stakeholders with a centralized view of ticket status.
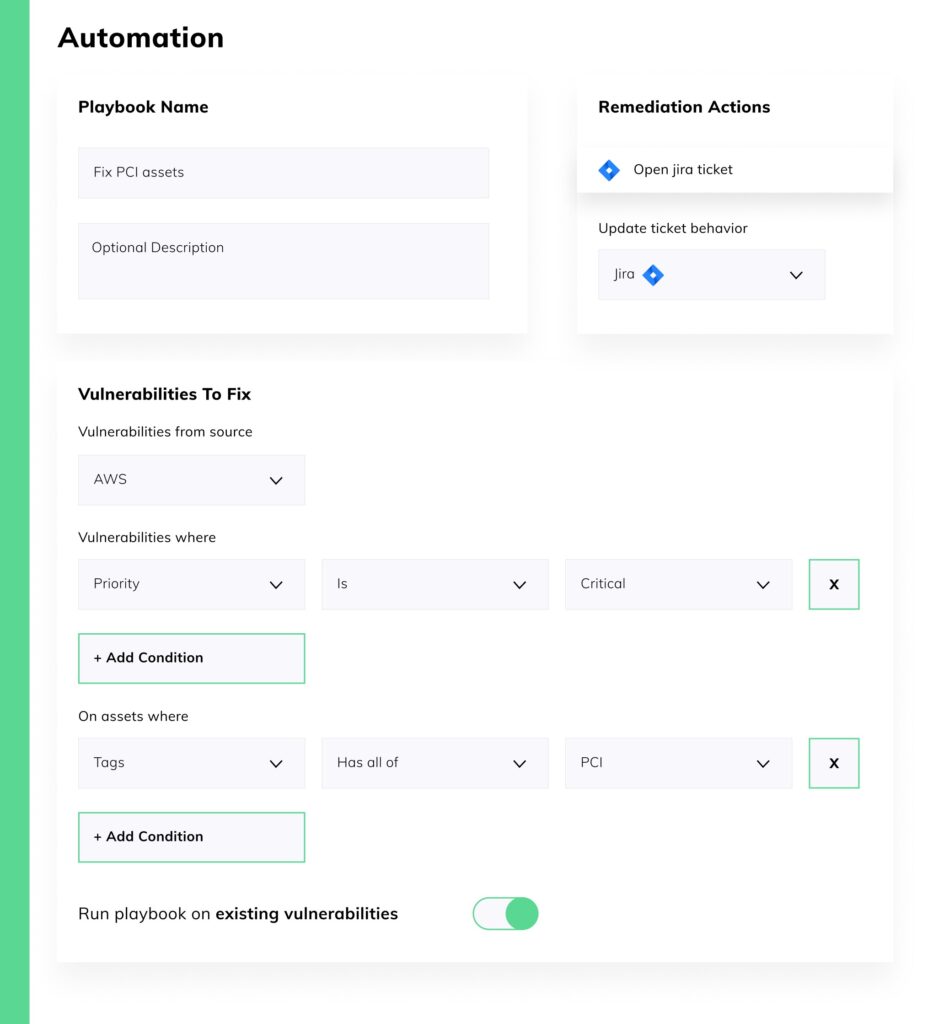
Tip:
Make sure that tickets contain all the information necessary to effectively resolve the vulnerability, including which assets are affected, active exploits, recommended patches or compensating controls, and so on.
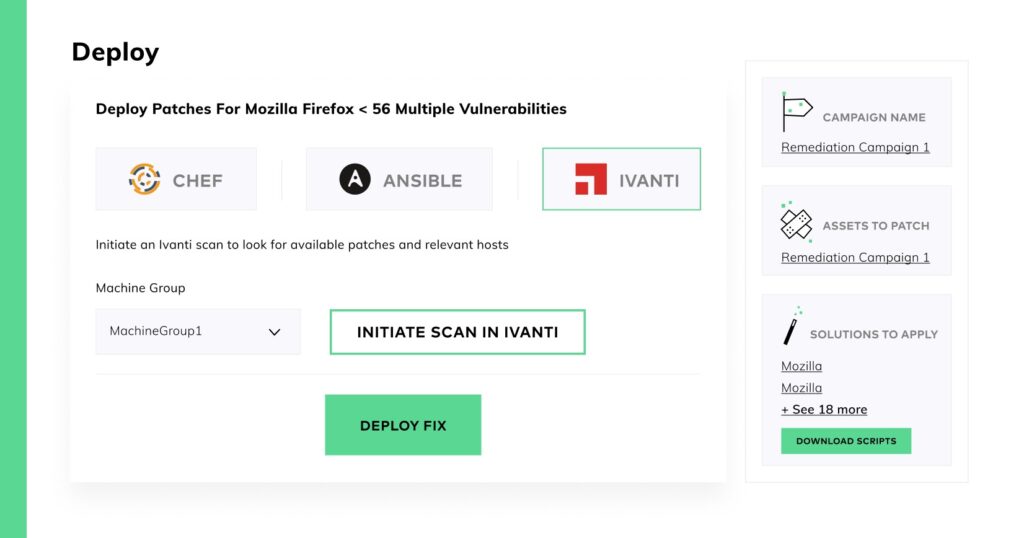
4. Automated Remediation
Yet another constraining factor in the vulnerability remediation process is choosing the right remediation measure and deploying it in a reliable, non-disruptive manner. Perhaps the vulnerability can be temporarily or permanently neutralized through a simple configuration change or compensating control. And if a patch is the required remedy, then which version and how can it be deployed safely into the production environment?
The solution:
Leverage IT automation tools such as Chef, Ansible, and Ivanti to run the required fix—be it a patch, configuration script, mitigating action, compensating control, or workaround. Be aware, however, that human intervention may be required at critical junctures such as deploying a patch into production.
At Vulcan Cyber, we hand teams the best remedy to get fix done and then create remediation scripts that can be plugged directly into the organization’s existing IT automation stack. We recommend automating the deployment of patches in testing environments as early as possible in the pipeline. By updating the testing environment with recent patches, the team can assess the latest changes and ensure that the target environment will handle the updates well, with little or no downtime.
Tip:
Capture repeatable vulnerability remediation workflows that are well suited to automation and then continuously monitor these baselines for optimization opportunities.
When to Proceed with Cyber Security Automation, with Caution
When it comes to cyber security automation and especially vulnerability remediation automation, there is no one-size-fits-all strategy. There are vulnerability remediation situations where automation may not be feasible at all, or they require significant human intervention:
- Many use cases to be validated: Sometimes a fix does not affect the main workflows but does interfere with other system use cases. It is very difficult to automatically test and validate all possible usage scenarios; human experience and expertise are required to analyze a fix’s overall impact.
- Non-redundant production environments: If the target environment has no redundancy and if there are stringent uptime SLAs to uphold, human supervision is critical in order to minimize downtime windows due to required system reboots or restarts. In these situations, it is also important that the team is on hand to immediately initiate a rollback procedure should the patch deployment be disruptive.
- Remediating business-critical environments: It’s one thing to have an automatically deployed patch disrupt the company’s lunch ordering app. It’s another story altogether when patching an environment that runs core business-critical workloads. In these cases, the team must closely scrutinize the remediation campaign and be ready to intervene as necessary.
- Patching environments without an easy rollback mechanism: In cases where there is no rollback mechanism in place or it would be very difficult to do a rollback, automation may not be a viable option. This may occur, for example, when there are non-deterministic factors that could affect system behavior.
About Vulcan
The powerful Vulcan remediation orchestration and security analytics platform hands teams the exact priorities, remedies, and cyber security automation they need to get fix done. Unlike typical vulnerability management tools that simply give you an endless to-fix list, Vulcan prioritizes based on both severity and fixability, hands you the ideal remedy for the job, then orchestrates and automates the entire fixing process. That’s why industry leaders like Snowflake, Clarivate, Informatica, and Blue Cross Blue Shield already use Vulcan to fix more vulnerabilities while spending 85% less time doing so.
Get fix done with Vulcan Remedy Cloud or request access to Vulcan Free. If you’d like more information before diving in, we’d be happy to provide a custom demo for your team.