-
Platform
OVERVIEW
Capabilities
-
Solutions
USE CASES
-
Cyber Risk Hub
LIBRARY
-
Company
GET TO KNOW US
-
Pricing
Learn the basics of security debt: What it is, how to identify it, and the best steps to reduce it effectively.

This blog aims to provide a detailed exploration of technical and security debt, offering insights into their origins, impacts, and strategies for mitigation. Through a careful examination of causes, manifestations, and remediation techniques, we’ll uncover how organizations can navigate the delicate balance between rapid innovation and the maintenance of robust, secure software systems.
Technical debt, a concept often encountered in the realm of software development, embodies the compromise between immediate functionality and the future cost of maintaining and upgrading the system. This metaphorical “debt” arises when decisions made for the sake of speed and expedience in development lead to additional, often greater, costs down the line. The interest on this debt manifests as the extra effort required to go back and resolve the shortcuts taken earlier.
While technical debt encompasses a broad spectrum of software development issues, a particularly critical aspect emerges when considering security vulnerability debt: this specifically refers to the compromises made that affect the security posture of a system, leaving it exposed to potential breaches and attacks.
Security vulnerability debt specifically addresses the backlog of unaddressed security risks that accumulate when the immediate demands of development lead to the postponement of necessary security measures. This backlog represents a growing list of vulnerabilities that, if left unmanaged, can expose systems to significant security breaches, compliance violations, and operational disruptions.
Both technical and security vulnerability debt can spring from various sources, ranging from intentional decisions made under pressure to reach market first, to inadvertent results of oversight or lack of foresight. Martin Fowler offers a nuanced classification:
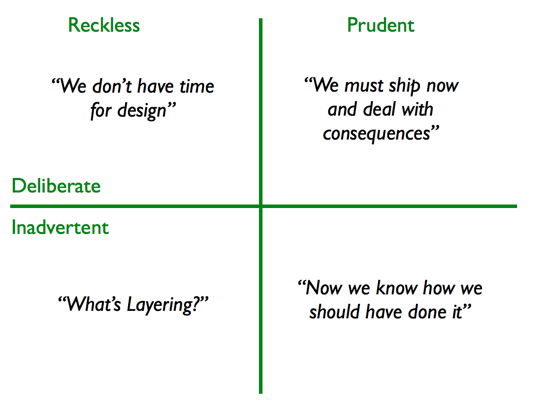
Security vulnerability debt is especially concerning because it directly impacts the risk profile of a software product, exposing users and organizations to potential harm.
Technical and security vulnerability debt share common causes, including but not limited to:
The consequences of unaddressed technical and security vulnerability debt are severe. Beyond the direct costs of remediation, which increase over time, there are broader implications:
In the context of cyber security, managing technical debt is not merely a matter of maintaining code quality and efficiency; it is a critical component of risk management and security posture. Addressing security vulnerability debt requires a proactive strategy, integrating security considerations into every stage of the development lifecycle and ensuring that decisions today do not compromise the security of the system tomorrow.
54%
of security leaders patched fewer than 50% of vulnerabilities in their backlogs in 2023.
The accumulation of security vulnerability debt poses significant challenges to organizations, threatening not only the integrity and efficiency of software systems but also their security posture. Effective management and mitigation of this debt are paramount to maintaining operational resilience, safeguarding data, and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. Herein lies a multifaceted approach to tackling both technical and security vulnerability debt.
The first step in addressing technical and security vulnerability debt is acknowledging its existence and comprehensively assessing its scope. This involves:
With a clear understanding of the debt landscape, organizations must develop a strategic plan for remediation that aligns with their business objectives and risk management priorities. This includes:
Mitigating security vulnerability debt requires the adoption of best practices throughout the software development lifecycle (SDLC):
A proactive approach to managing security vulnerability debt involves cultivating a culture of security within the organization:
Utilizing the right tools can significantly enhance an organization’s ability to manage vulnerability management programs effectively.
Managing security vulnerability debt is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and adaptation:
Security vulnerability debt can severely impair a company’s ability to innovate, can harm brand image, and severely impact your bottom line. Adopting best practices including proper testing, effective patch management, and a DevSecOps approach can help you avoid security debt and keep your customers’ data safe.
The Vulcan Cyber® ExposureOS prioritizes and automates the entire vulnerability management process across every stage of the lifecycle. It integrates with your existing tools and security solutions—from asset management, testing, and patching to DevOps tools, ITSM, and configuration management. Vulcan Cyber lets you fix security vulnerabilities early in the production process and at scale to deliver secure code at speed, without disrupting business operations.