-
Platform
OVERVIEW
Capabilities
-
Solutions
USE CASES
-
Cyber Risk Hub
LIBRARY
-
Company
GET TO KNOW US
-
Pricing
This blog explores the OWASP top 10 vulnerabilities for 2022 - together with what we learned and how you can protect against them.
In the rapid-fire environment of today’s development cycles, security can often be left as a checkbox item without any real consideration. Understanding the vulnerabilities that can be built into applications is a good place to increase overall security hygiene. The OWASP Foundation puts out the OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities list to help organizations and developers accomplish this.
The OWASP Top 10 is a collection of security vulnerabilities reported from actual web application data and other sources. The list provides detailed information about these vulnerabilities, including examples of each.
In this blog, we’ll dive into each point in the OWASP Top 10 2022 list and look at security precautions organizations can adopt to prevent these risks.
The OWASP Top 10 is put out by the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) Foundation. OWASP is a non-profit organization with a mission to bolster software security across industries. To further that mission, OWASP maintains and publicly shares the OWASP Top 10, an awareness document for web application security vulnerabilities.
For each ranking period, OWASP collects application data from a variety of sources and conducts a survey to gather important information about the top vulnerabilities developers encounter, but that may not be expressed in the application data received. These are usually trends developers observe that may have the potential to cause damage.
Submitted web application data and survey results are used together to rank the top ten security vulnerabilities.
Vulnerabilities are ranked based on a range of factors, which include analysis of actual web application data submitted by individuals and organizations. Contributed data can be attributed to companies/organizations or kept pseudo-anonymous.
Data sources also include bug bounty programs, security consultancies, and vendors. Contributors provide details of the time period for the data, the total number of web applications, and the list of common weakness enumerations (CWEs) as defined by MITRE. Contributors must also provide the number of applications containing each core CWE.
During analysis, OWASP finds the number of applications with one or more instances of a CWE. The incidence rate is calculated by totaling all the applications that were tested and then comparing that number to the total number of applications where a CWE occurred.
The top ten results are then ranked based on additional input from the accompanying survey of application and security experts. Analysis focuses on the root cause of vulnerabilities above the symptom whenever possible.
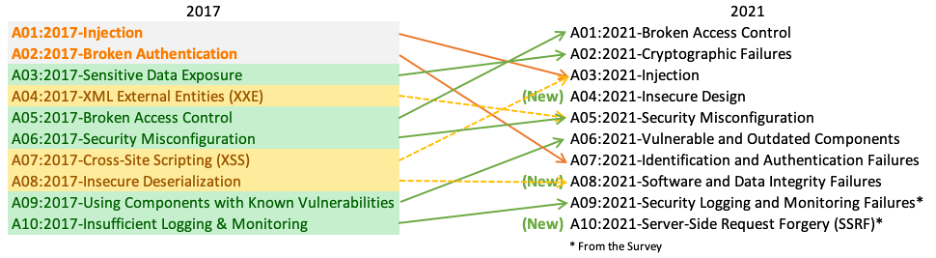
The OWASP Top 10 for 2021 contained more application data than any previous report the foundation had put out: A record 500,000 applications were submitted. The 2021 list was also the most data-driven version. The data volume required a shift in how the project categorized vulnerabilities.
These new categories were created to highlight trends in application data and to provide additional training benefits for companies that focus on specific CWEs related to the programming languages or frameworks they actively use.
Access control limits what users can access, restricting them to resources within their assigned permissions. Access control failure commonly results in users performing business functions requiring different permissions than they were assigned, among other activities. Failure also leads to unauthorized information disclosure, modification, or data destruction.
Access control vulnerabilities include:
Limit access to resources with access control. Access control works in a trusted server environment where data cannot be modified by the attacker. Protection methods include:
Rate-limit API and controller access.
Cryptographic failures are a broad symptom of a breakdown or deficiency in cryptography, which can lead to system compromise or sensitive data exposure. Personally identifiable data and credit card numbers are among the data types that require extra protection.
Data protection methods are determined by the type of data and whether or not it is subject to data privacy laws such as the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Cryptographic failures include:
Preventing cryptographic failure depends on application functionality and the type of data used. There are a wide range of aspects to protecting data appropriately. Prevention includes the following (and much more, which is covered in OWASP reference guides):
Injection vulnerabilities can be detected through source-code review. This category includes cross-site scripting, SQL injection, and XML injection, among many others. Automation can help here by making sure all parameters and data inputs are tested to identify vulnerabilities.
Applications are vulnerable to injection when:
Keeping queries and commands separate from data is critical to preventing attempts at injection:
Insecure design differs from insecure implementation. A secure design can be implemented imperfectly, resulting in vulnerabilities. However, an insecure design can’t be fixed through implementation since the design itself doesn’t contain appropriate security controls.
A failure to accurately assess business risk associated with the software or system under development leads to insufficient levels of security.
A culture of security includes using a secure design methodology that evaluates threats and ensures code is designed and tested against known attack methods. Prevention includes methods that foster a secure development culture:
Security misconfigurations can be caused by an array of inappropriately configured controls as well as other factors which contribute to application vulnerability. This category includes many common misconfigurations:
Prevention begins with a thorough security configuration process that is repeatable across systems and preferably automated:
White paper: Cloud security risks in 2022, where we stand?
Unpatched and legacy components that remain in production well after vulnerabilities are discovered and disclosed can be a major risk. Applications can be vulnerable when they aren’t running the latest software version. If it’s unclear which library or component version is being used, the application may be vulnerable. Components that aren’t scanned for vulnerabilities may also be at risk.
Establishing a patch-management process can help alleviate the potential for attack by closing vulnerabilities before they become an issue. This should include:
Authentication and identification failures happen when user identity, authentication, and session information aren’t confirmed before the user is permitted to access systems and data. Factors that may put an application at risk due to these failures include allowing weak passwords, using weakly hashed, plain-text password data stores, and allowing bots, which can perform automated attacks such as brute-force and credential stuffing.
Prevention focuses on providing secure password storage and retrieval and includes:
New to the OWASP list is the CWE of failures in software and data integrity. The risk here is trusting data and software updates without checking their integrity. Attackers have used the software supply chain to issue malware through seemingly legitimate software updates. Many systems use automated software update features that do not verify the integrity of updates.
Prevention begins with verification and includes:
Verifying that third-party resources contain no vulnerabilities, by using automated security tools designed for the software supply chain.
The security logging and monitoring failures category focuses on issues with audit logs and monitoring during an attack. Security monitoring and logs are essential to detect and mitigate an active breach. Failures happen when:
Prevention focuses on enabling security logging and monitoring across applications. Developers should ensure security controls are implemented where appropriate. Security controls should include the following:
The server-side request forgery category focuses on weaknesses within user-convenience features. SSRF flaws happen when web applications fetch user-requested remote sources without first verifying the destination. Specific requests can be sent to the application through an unexpected source.
Applications commonly fetch URLs to enable easier task switching for end-users, often keeping them in the application while providing access to another feature through the fetched URL. Ever-increasing cloud architecture complexity means SSRF is occurring at a higher frequency.
SSRF occurs at the network and application levels. Protect networks by using network segmentation to separate remote resources. Block other nonessential traffic with “deny-by-default” policies.
Application protection methods should include:
Read report: Vulcan Cyber named a Leader by Forrester for Vulnerability Risk Management
Traditionally, security is difficult to incorporate into development processes. If DevSecOps isn’t an option for the organization or development process/stage, security tools can help surface issues early so they can be addressed.
Design with security in mind. Security contributes to an application’s overall security success since securely designed apps prevent attackers from wreaking havoc, ensure compliance requirements are met, and help build consumer trust.
White paper: Secure coding best practices you should know about
Application security best practices focus on controlling who has access to information and systems while also accounting for secure data storage and transmission. Application logs provide historical records of system and network activity.
Balancing security against tight deadlines can be challenging, especially in today’s fast-paced development environments. Application security is an ongoing process that requires deliberate action to achieve. The OWASP Top 10 2022 is an invaluable resource of known and possible vulnerabilities for development teams looking to create secure web applications.
It’s important to prioritize application vulnerabilities by considering business impact in addition to other aspects of the overall threat profile. A threat that is extremely likely to happen but has minor consequences may be important to address before a threat that is extremely unlikely to happen but would have major consequences.
The OWASP Top 10 can help you identify where to strengthen your security, but making sure that happens is up to you.Find the threats that matter to your business application environments. The Vulcan Cyber® risk management platform helps you make informed decisions so you can own your risk. Find out more about our application security programs or request a demo.
OWASP stands for the Open Web Application Security Project. It is a nonprofit organization that works to improve the security of software and web applications. OWASP provides resources, tools, and guidelines for developers, security professionals, and organizations to help them build and maintain secure applications.
2003.
Every three to four years.
OWASP was created to improve the security of software and web applications. The project was founded in 2001 by a group of like-minded individuals who recognized the need for a collaborative effort to address the growing security threats facing web applications.
At the time, there was little emphasis on security during the software development process, and most security measures were implemented after the application had been deployed. The founders of OWASP believed that this reactive approach to security was insufficient and that security should be integrated into the software development process from the beginning.
OWASP was established as a non-profit organization to provide developers, security professionals, and organizations with resources, tools, and guidelines to help them build and maintain secure applications. The organization has since grown to become a global community of professionals and volunteers who work together to promote best practices, education, and awareness in the field of web application security.